
Rehydrate
Rehydration should occur immediately following exercise
Every 1kg of weight lost should be replaced with 1.5 litres of fluid
Consume over 4 hours and avoid alcohol as it is counter productive to recovery
Examples include water, carbohydrate electrolyte drinks such as lucozade, milk, electrolyte drinks such as high 5 zero
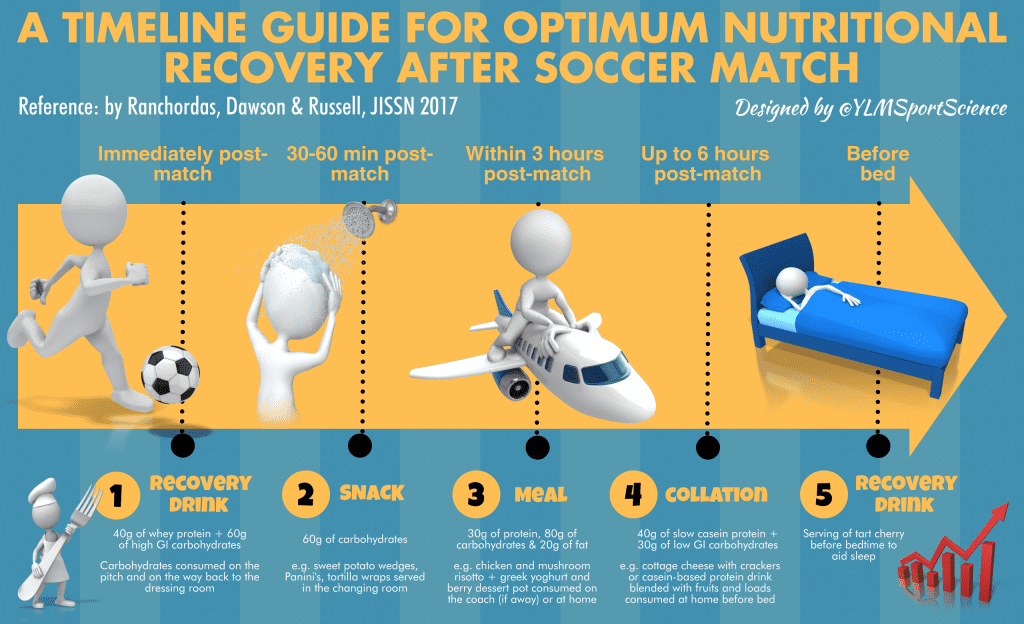
Ranchordas, Dawson and Russell (2017)
Refuel
Immediately post match consume simple carbohydrates (high glycemic index) to begin replenishing glycogen store such as carbohydrate electrolyte drinks, gels, cereal bars, fruit
Research shows protein alongside carbohydrate stimulates glycogen synthesis to a great extent e.g. protein shake / bar, milk, yoghurt
2-3 hours post match consume a meal with complex carbohydrates (low glycemic index) and protein to continue refuelling in preparation for the following days / weeks training e.g. tuna pasta, chicken and rice, protein oats, eggs on wholewheat toast
Ranchordas, Dawson and Russell (2017)
Repair
Protein intake aids the repair and regeneration of muscle tissue
Protein intake should be divided into 6x 20-25g servings (depending on bodyweight) over the day to maximise protein synthesis
Examples providing 20g of protein include 1 chicken breast, 3 large eggs, 1 scoop of protein powder, 80g canned tuna, 200g tub of fat free yoghurt, 200g of cottage cheese
Ranchordas, Dawson and Russell (2017)
Relax
1.7 times greater risk of being injured in athletes who sleep less than 8 hours
Sleep loss is associated with poor cognitive performance
Light exposure from electronic displays can affect sleep – put your phones away before bed
Le Meur, Skein and Duffield (2013)
